OpenMRS is a free and open-source project to develop software for delivering health care in developing countries. It is an enterprise electronic medical record system framework that allows the exchange of patient data with other medical information systems. It is written in Java and provides a web interface to manage electronic medical records.
In this post, we will show you how to install OpenMRS on Ubuntu 20.04.
Prerequisites
- A Ubuntu 20.04 VPS with root access enabled or a user with sudo privileges.
Log in via SSH and Update your System
First, you will need to log in to your Ubuntu 20.04 VPS via SSH as the root user:
ssh root@IP_ADDRESS -p PORT_NUMBER
Next, run the following commands to upgrade all installed packages on your VPS:
apt-get update -y
Once all the packages are updated, restart your system to apply the changes.
Install Java 8
OpenMRS is a Java-based application and only supports Java version 8. So you will need to install Java 8 on your server. You can install it by running the following command:
apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk -y
Once Java is installed, verify the Java version using the following command:
java -version
You will get the following output:
openjdk version "1.8.0_312" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_312-8u312-b07-0ubuntu1~20.04-b07) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.312-b07, mixed mode)
Install MySQL Server 5.6
OpenMRS only supports MySQL version 5.6. By default, MySQL 5.6 is not available in the Ubuntu 20.04 default repository. So you will need to install it from the source.
First, create a user and group for MySQL using the following command:
groupadd mysql useradd -g mysql mysql
Next, download MySQL 5.6 source with the following command:
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.6/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
Once the MySQL is downloaded, extract it with the following command:
tar -xvf mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
Next, move the extracted directory to /usr/local with the following command:
mv mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /usr/local/mysql
Next, navigate to the /usr/local directory and set proper ownership with the following command:
cd /usr/local/mysql chown -R mysql:mysql *
Next, install the required dependencies using the following command:
apt-get install libaio1 libncurses5 libnuma-dev -y
Next, install MySQL with the following command:
scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql
Next, set proper ownership to MySQL directory and data directory:
chown -R root . chown -R mysql data
Next, copy the MySQL configuration file and service file:
cp support-files/my-default.cnf /etc/my.cnf cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysql.server
Next, start the MySQL service in safe mode:
bin/mysqld_safe --user=mysql &
Next, set the MySQL root password with the following command:
bin/mysqladmin -u root password newpassword
Next, create a link of the MySQL binary:
ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/local/bin/mysql
Finally, restart your server with the following command:
reboot
After the reboot, start the MySQL service and enable it to start at system reboot:
/etc/init.d/mysql.server start update-rc.d -f mysql.server defaults
Install Tomcat 7
First, create a user and group for Tomcat with the following command:
groupadd tomcat useradd -s /bin/false -g tomcat -d /opt/tomcat tomcat
Next, download the Tomcat 7 with the following command:
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-7/v7.0.109/bin/apache-tomcat-7.0.109.tar.gz
Next, create a directory for Tomcat and extract the downloaded file to /opt/tomcat directory:
mkdir /opt/tomcat tar -xvzf apache-tomcat-7.0.109.tar.gz -C /opt/tomcat/ --strip-components=1
Next, navigate to the /opt/tomcat directory and set proper permission and ownership:
cd /opt/tomcat chgrp -R tomcat /opt/tomcat chmod -R g+r conf chmod g+x conf chown -R tomcat webapps/ work/ temp/ logs/
Create a Systemd Service File for Tomcat
Next, you will need to create a systemd service file to manage the Tomcat service. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Add the following lines:
[Unit] Description=Apache Tomcat Web Application Container After=network.target [Service] Type=forking Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-amd64 Environment=CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/temp/tomcat.pid Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat Environment=CATALINA_BASE=/opt/tomcat Environment=’CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512M -Xmx1024M -server -XX:+UseParallelGC’ ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/startup.sh ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh User=tomcat Group=tomcat UMask=0007 RestartSec=10 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file then reload the systemd daemon to apply the changes:
systemctl daemon-reload
Next, start the Tomcat service with the following command:
systemctl start tomcat
You can now check the status of the Tomcat service with the following command:
systemctl status tomcat
You will get the following output:
● tomcat.service - Apache Tomcat Web Application Container
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2022-02-23 08:48:12 UTC; 6s ago
Process: 10027 ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/startup.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 10049 (java)
Tasks: 28 (limit: 4686)
Memory: 94.1M
CGroup: /system.slice/tomcat.service
└─10049 /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-amd64/bin/java -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/opt/tomcat/conf/logging.properties -Djav>
Feb 23 08:48:12 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Starting Apache Tomcat Web Application Container...
Feb 23 08:48:12 ubuntu2004 startup.sh[10027]: Tomcat started.
Feb 23 08:48:12 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Started Apache Tomcat Web Application Container.
At this point, Tomcat is started and listens on port 8080.
Install OpenMRS
First, create a directory for OpenMRS and set proper ownership with the following command:
mkdir /var/lib/OpenMRS chown -R tomcat:tomcat /var/lib/OpenMRS
Next, download the latest version of OpenMRS using the following command:
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/openmrs/files/releases/OpenMRS_Platform_2.5.0/openmrs.war
Once the download is completed, copy the downloaded file to the Tomcat webapps directory:
cp openmrs.war /opt/tomcat/webapps/
Next, change the ownership of the openmrs.war file to tomcat:
chown -R tomcat:tomcat /opt/tomcat/webapps/openmrs.war
Access OpenMRS Installation Wizard
Now, open your web browser and access the OpenMRS web installation wizard using the URL http://your-server-ip:8080/openmrs. You should see the OpenMRS language selection screen:
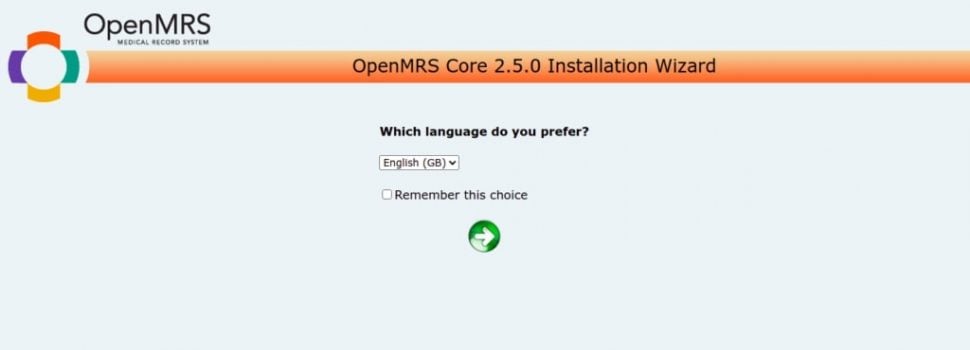
Select your language and click on the => button. You should see the Installation Type screen.
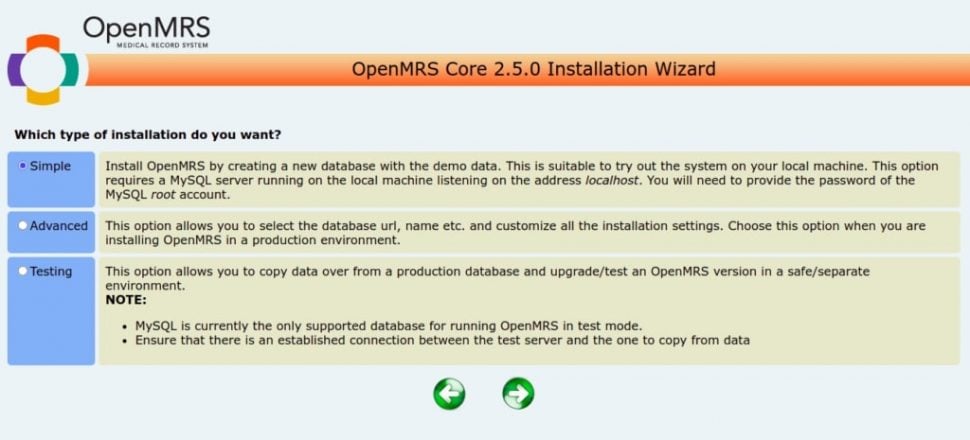
Select the type of installation you want and click on the => button. You should see the following screen:
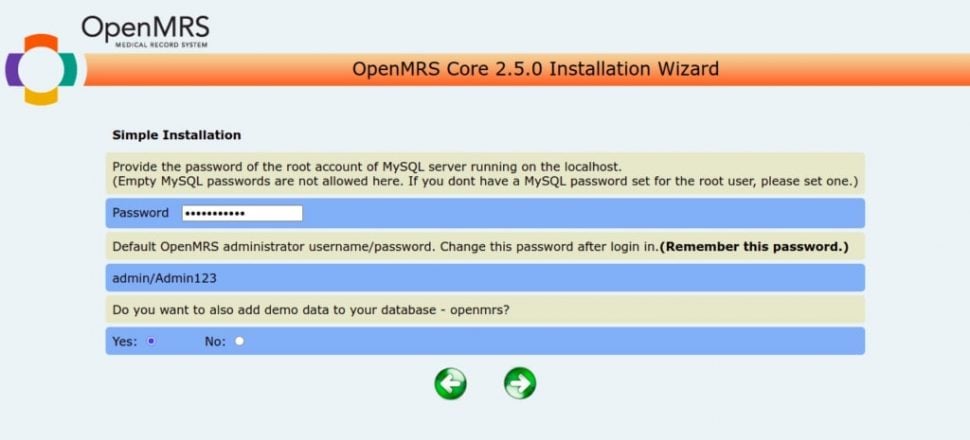
Provide your MySQL root password, note down the admin password, and click on the => button. You should see the following screen:
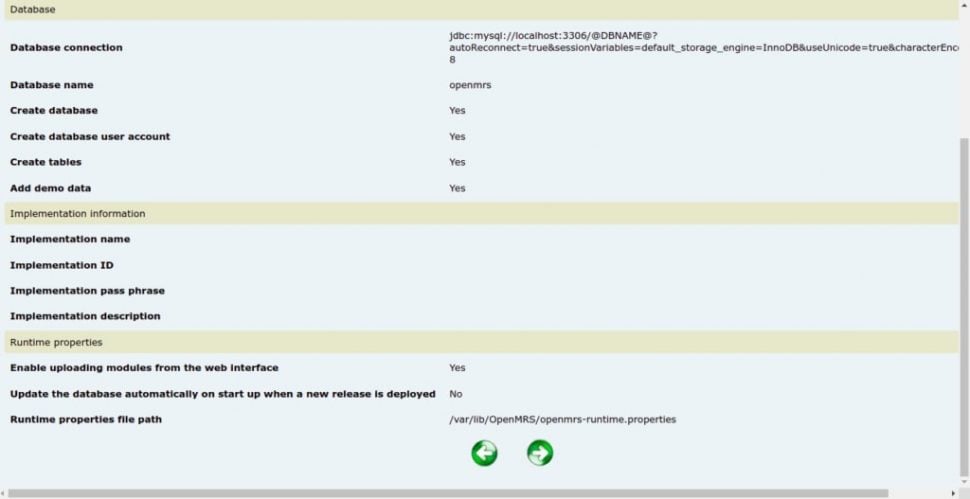
Click on the => button to create a database for OpenMRS and complete the installation.
Now, open your web browser and access the OpenMRS admin interface using the URL http://your-server-ip:8080/openmrs. You should see the OpenMRS login screen:

Provide the default username as admin and password as Admin123, then click on the LOG IN button. You should see the OpenMRS dashboard on the following screen:
We hope that our step-by-step guide on installing OpenMRS has made the process much clearer and easier for you. Now, we’d love to hear from you:
Do you have any concerns about the steps or need more detailed information? Can you suggest other areas of interest or step-by-step tutorials that you would like us to explore in our future posts?
We’d appreciate your feedback in the comments below.

Please help me on how to install modules, I have tried a lot but it’s not working so far. I have downloaded the OpenMRS modules and then copy them to /var/lib/OpenMRS/modules and restarted tomcat but no any change. I still get the same interface “If you are seeing this page, it means that the OpenMRS Platform is running successfully, but no user interface module is installed. Learn about the available User Interface Modules”